Betelgeuse's Mysterious Behavior Explained by Hidden Companion Star's Wake
7 minutes Read
Introduction
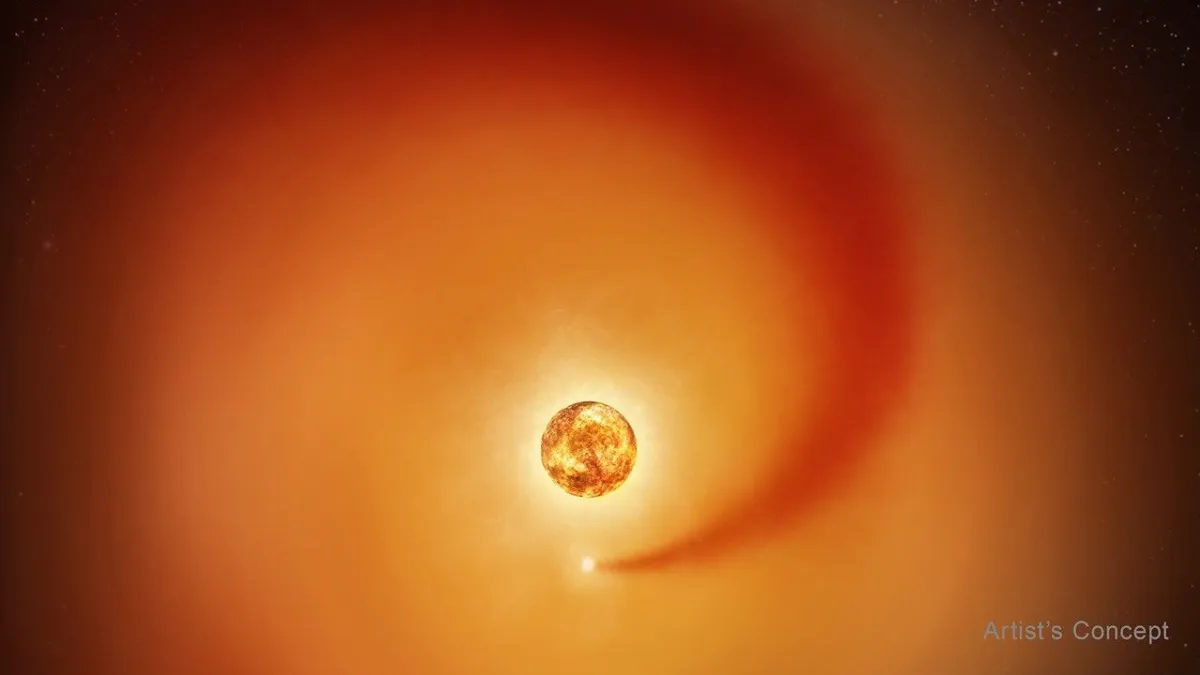
Astronomers have long been captivated by the enigmatic red supergiant star Betelgeuse, observing peculiar changes in its brightness and atmosphere. New research, utilizing data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories, has revealed a significant clue to these mysteries: a dense trail of gas swirling through Betelgeuse’s extensive atmosphere. This discovery points to the influence of a recently identified companion star, named Siwarha, and offers a compelling explanation for the giant star's unusual behavior.
The findings, presented by scientists from the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), shed light on the complex evolution of massive stars. By meticulously tracking changes in Betelgeuse’s light over nearly eight years, the research team detected the signature of Siwarha’s wake. This wake is formed as the companion star plows through the outer layers of Betelgeuse, a phenomenon that helps resolve long-standing questions about the star's dynamics and its eventual fate.
Unveiling the Companion's Influence
Betelgeuse, situated approximately 650 light-years away in the constellation Orion, is a colossal red supergiant star so immense that over 400 million Suns could fit within its volume. Its sheer size and relative proximity to Earth make it a unique celestial laboratory, allowing astronomers to directly observe its surface and surrounding atmosphere. This makes Betelgeuse a crucial target for understanding how stars of its kind age, shed mass, and ultimately conclude their lives in spectacular supernova explosions.
The team's investigation combined observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope with data from ground-based observatories, including the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory and Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory. This multi-faceted approach allowed them to discern a pattern of changes in Betelgeuse that provided clear evidence for a suspected companion star and its profound impact on the red supergiant's outer atmosphere. These changes were evident in the star's spectrum—the specific colors of light emitted by different elements—and in the speed and direction of gases within its outer atmosphere, all attributed to a trail of denser material, or wake. This wake appears consistently after the companion star passes in front of Betelgeuse approximately every six years, or roughly 2,100 days, a timing that aligns with theoretical predictions.
A Stellar Boat and Its Wake
“It’s a bit like a boat moving through water. The companion star creates a ripple effect in Betelgeuse’s atmosphere that we can actually see in the data,” explained Andrea Dupree, an astronomer at the CfA and lead author of the study. She further elaborated, “For the first time, we’re seeing direct signs of this wake, or trail of gas, confirming that Betelgeuse really does have a hidden companion shaping its appearance and behavior.” This direct evidence provides a crucial piece of the puzzle that has occupied astronomers for decades as they tried to understand Betelgeuse's fluctuating brightness and surface features. The star's unexpected dimming in 2020, a phenomenon dubbed a "sneeze," had particularly intensified scientific curiosity.
Scientists had previously considered various explanations for Betelgeuse's variable behavior, including large convection cells, dust clouds, magnetic activity, and the possibility of an unseen companion. While recent studies had suggested that the long-term variations in Betelgeuse’s light were best explained by a low-mass companion orbiting deep within its atmosphere, concrete proof remained elusive. The detection of Siwarha's wake now offers this definitive evidence, confirming that a companion star is indeed disrupting the atmosphere of this massive supergiant.
Future Observations and Broader Implications
The confirmation of Betelgeuse's companion star opens up new avenues for research. With Betelgeuse currently obscuring the companion from our direct view, astronomers are eagerly anticipating its next emergence in 2027 for further observations. This breakthrough is not only significant for understanding Betelgeuse but also holds the potential to illuminate similar mysteries observed in other massive and supergiant stars. By studying how Betelgeuse evolves, sheds material, and ultimately undergoes a supernova, scientists can gain invaluable insights into the life cycles of these celestial giants. The Hubble Space Telescope, a testament to international collaboration between NASA and ESA, continues to be instrumental in these groundbreaking discoveries, shaping our fundamental understanding of the universe.
Original source: "https://science.nasa.gov/missions/hubble/nasa-hubble-helps-detect-wake-of-betelgeuses-elusive-companion-star"